Há plástico na sua comida – veja como reduzir sua ingestão
Resumo:
* Microplastics have been found in the human brain, and people may consume around 74,000 to 121,000 microplastic particles each year.
* The long-term health effects of microplastics in food are still being investigated.
* Foods like seafood, tea, rice, salt, sugar, bottled water, honey, fruits and vegetables, and proteins can contain microplastics.
* Some tips to reduce microplastic intake include minimizing shellfish consumption, avoiding plastic food storage containers and wraps, using non-plastic kitchen utensils, and washing clothes with filters.
“`
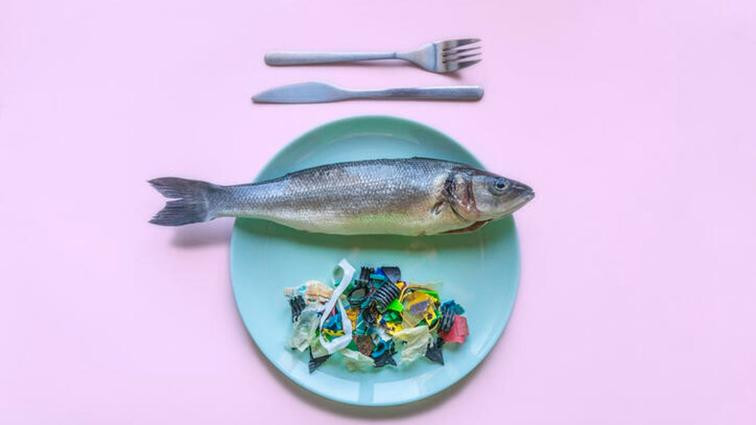
Microplastics are everywhere, including in our food. A study found a whole plastic spoon’s worth of tiny plastic shards in human brain tissue.
While the long-term health effects of microplastics in food are still being investigated, it’s a good idea to minimize exposure where possible. Here’s a summary of foods that may contain microplastics and tips to reduce intake:
- Seafood: Microplastics enter our food through single-use plastics that break down and find their way into waterways and soil, ending up in seafood.
- Tea: Plastic in tea bags can release microplastics into your tea.
- Rice: Rice can contain microplastics, especially instant rice.
- Salt and sugar: Microplastics have been found in both salt and sugar.
- Bottled water: Water bottles contain micro and nanoplastics that can be ingested.
- Honey: Microplastic fibers can be found in honey.
- Fruits and vegetables: These can contain microplastics from soil or packaging.
- Proteins: Both animal and plant-based proteins can contain microplastics.
To reduce microplastic intake, consider the following tips:
- Be careful with shellfish consumption, as they have higher levels of microplastics.
- Avoid food-storage containers and plastic wraps to minimize exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals.
- Get rid of plastic kitchen utensils and opt for ceramic, glass, stainless steel, or wood alternatives.
- Install a filter in your clothes-washing machine to catch microfibers before they pollute water systems.
While we still have a lot to learn about microplastics and their long-term implications, maintaining a balanced diet will ensure our bodies have enough fuel to function and thrive.

“`
Por favor, ignore o código HTML fornecido anteriormente e utilize o resumo e o texto reformulado a seguir para criar um novo bloco de código HTML.
“`html
Resumo:
* Microplasticas estão presentes em nosso cérebro e podemos ingerir até 74.000 a 121.000 partículas de microplástico por ano.
* Os efeitos a longo prazo das microplásticas na alimentação ainda estão sendo investigados.
* Alimentos como frutos do mar, chá, arroz, sal, açúcar, água engarrafada, mel, frutas e legumes e fontes protéicas podem conter microplásticas.
* Algumas dicas para reduzir a ingestão de microplásticos incluem diminuir o consumo de frutos do mar, evitar o uso de recipientes e embalagens plásticas, utilizar talheres não plásticos e lavar roupas com filtros.
As microplásticas estão presentes em todos os lugares, inclusive em nossa alimentação. Um estudo encontrou uma colher cheia de fragmentos de plástico pequenos no tecido cerebral humano.
Enquanto os efeitos a longo prazo das microplásticas na alimentação ainda estão sendo investigados, é uma boa ideia minimizar a exposição onde possível. Aqui está um resumo dos alimentos que podem conter microplásticas e dicas para reduzir a ingestão:
- Frutos do mar: As microplásticas entram em nossa comida através de plásticos de uso único que se degradam e encontram seu caminho em água e solo, acabando em frutos do mar.
- Chá: O plástico presente nas sacos de chá pode liberar microplásticas em seu chá.
- Arroz: O arroz pode conter microplásticas, especialmente o arroz instantâneo.
- Sal e açúcar: As microplásticas foram encontradas tanto no sal quanto no açúcar.
- Água engarrafada: As garrafas de água contém micro e nanoplast

 ×
×